There are quite a few different types of semiconductor diode from junction diodes, Schottky diodes, Zener diodes etc. You need to know the difference between them in order to select one. A good place to start the description of the types would be a comparison of a conventional PN junction diode and a fast recovery […]
FAQ
What are amplifier classes and their power efficiencies?
Amplifiers which must produce significant output power face challenges of performance and efficiency. The industry has some long-established designations for classes of amplifiers as well as some relatively new classes. First a look at the older but still widely used classes commonly known as A, B, AB, C, and D. The Class A amplifier provides […]
Ode to reliable USB connectors
Because our work depends so much on the technologies we utilize, one of our year-end reviews covers a post-mortem summary of all failures related to our equipment use. The summary includes system failures, which are thankfully rare, and also encompasses use-model failures such as our discovery that the RF data-link receivers we use on location […]
The 10 most popular posts on Power Electronic Tips for 2016
We went into our article archives to uncover the most widely read posts on powerelectronictips.com over the past 12 months. Here for your reading (or re-reading?) pleasure are the top 10 stories: Teardown: What’s inside a Phillips Sonicare electric toothbrush? How and when MOSFETS blow up Gallery: Scenes from Texas Instruments’ power supply design seminar […]
Less famous attributes of Schottky diodes
Schottky diodes are useful in some power-converter topologies, especially for shunting the body diode in a half-bridge’s low-side MOSFET. In this position, the Schottky diode prevents the body diode from turning on, particularly when driving inductive loads common in power converters, because it’s forward voltage drop is smaller than that of the body diode’s PN […]
When should I use an LDO versus a switching regulator?
Both switchers and LDOs have their place in power distribution, as each has special attributes. With few exceptions, every electronic circuit needs at least one well-regulated, accurate, stable dc power rail at 12, 5, 3.3 V, or even at 1 V, and many systems need five, ten or more such rails. This power must come […]
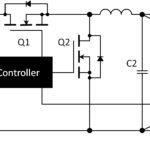
What is the MOSFET body diode?
Unlike virtually every other active device, the power MOSFET is unusual in that its schematic symbol includes a parasitic device – the body diode. The body diode is intrinsic to the device’s structure. It remains despite a number of fundamental changes in power MOSFET structure and device designs including the two most common types today […]
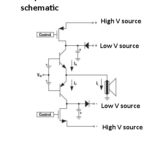
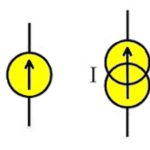
Current sources and why we need them
Engineers are all familiar and comfortable with voltage sources such as batteries or ac/dc supplies. The function of a voltage source, represented by a simple symbol is clear: Provide as little or as much current as needed (up to a maximum current limit) at a given, defined voltage; this voltage value may be fixed or […]
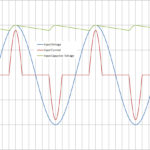
Basics of understanding power factor and power factor correction
In qualitative terms, power factor is a measure of the congruency of voltage and current ac waveforms imposed by a load on the power mains. Ignoring the relative phase of the two waveforms, the apparent power (S) is the simple product of the waveform amplitudes, S = V × I. Limiting our focus for now […]
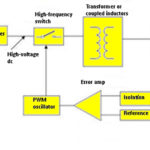
What are the benefits of 48 V distribution?
Mains-connected computational resources have been powered primarily by 12-V distribution feeds for decades. The 12-V distribution potential has been a convenient choice because it lets designers route power efficiently throughout small-to-medium-sized systems and operate inexpensive, off-the-shelf fans and disk drives directly from the distribution voltage. Advances in the semiconductor fabrication process have driven significant reductions […]